Large String Variable
In most cases, for strings up to 1 MB in size, using the standard String variable type is sufficient. However, for strings greater than 1 MB in size that are needed as inputs to other activites in your workflow, use the Large String variable type that supports strings up to 10 MB in size.
For example, use this if you expect a very large JSON response body from an HTTP call. When you send an HTTP request and expect a very large response body in return, use the core Set Variables activity (update a variable value based on data retrieved in a workflow) to assign that to a Large String variable which you can then use in a following activity within your workflow.
At the end of a workflow execution, data stored in the Large String variable is not displayed, but can be downloaded to your device. In the workflow properties, click on a variable to view its configuration. To save the value of the variable to your device, click Download.
Currently, the system supports up to three Large String variables per workflow.
-
Importing and exporting a workflow that has a Large String variable is allowed. However, it is not supported with a Large String value stored in the variable definition and will generate an error.
-
When using Large String variables, be mindful of the additional processing time required and how it may potentially surpass timeouts.
-
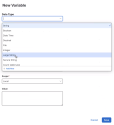
When adding or editing a variable from the Workflow Editor, choose Large String from the Data Type drop-down list.
-
Enter a meaningful Display Name.
-
The Scope can be Local, Static, Input, or Output.
-
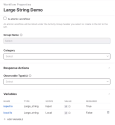
At this point in defining the workflow variable, you will not enter a value for the large string. Click Save. The value will be entered during the runtime of the workflow, if an action results in passing or the user is passing a value as an input variable to another activity or sub-workflow.
-
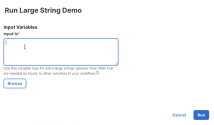
Run the workflow, and instead of entering the large string in the text box for the input variable, click Browse and choose the file containing the large string. After it's entered, click Run to continue.
-
Set Variables
-
XPath Query
-
JSONPath Query
-
Escape Regex Metacharacters
-
Find String
-
Convert Json to Xml
-
Match Regex
-
Replace String
-
Substring
-
Trim String
-
XSL Transform
-
Execute Python Script
-
Read Table from JSON
-
Read Table from Text
-
Read Table from XML
-
HTTP Request (only "body" property)
-
Swagger HTTP Request (only "body" property)